This chapter is a detailed section of Chapter 19. Please read Chapter 19, Nanboku-cho Period Tanto, before proceeding on to this part.

The red circle above indicates the time we discuss in this section

The drawing above shows a typical shape of a Nanboku-cho-period tanto. This drawing was in Chapter 19. I exaggerated the features of the Enbun Joji ko-wakizashi tanto to better show you. At the end of Chapter 19, Nanboku-cho Tanto, there is a list of swordsmiths’ names from that period. Hiromitsu (広光) and Akihiro (秋広) represent the Nanboku-cho style.

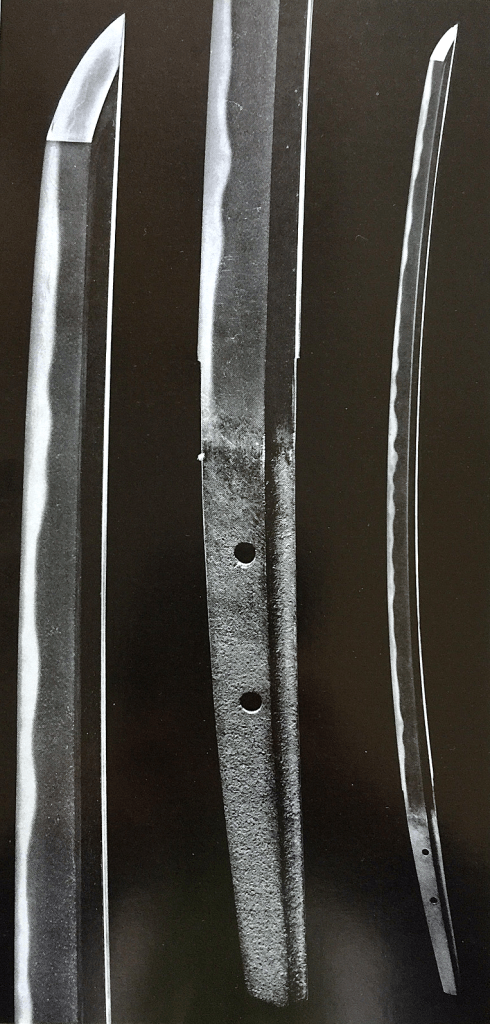
 Hiromitsu from the Sano Museum Catalogue (permission to use granted)
Hiromitsu from the Sano Museum Catalogue (permission to use granted)
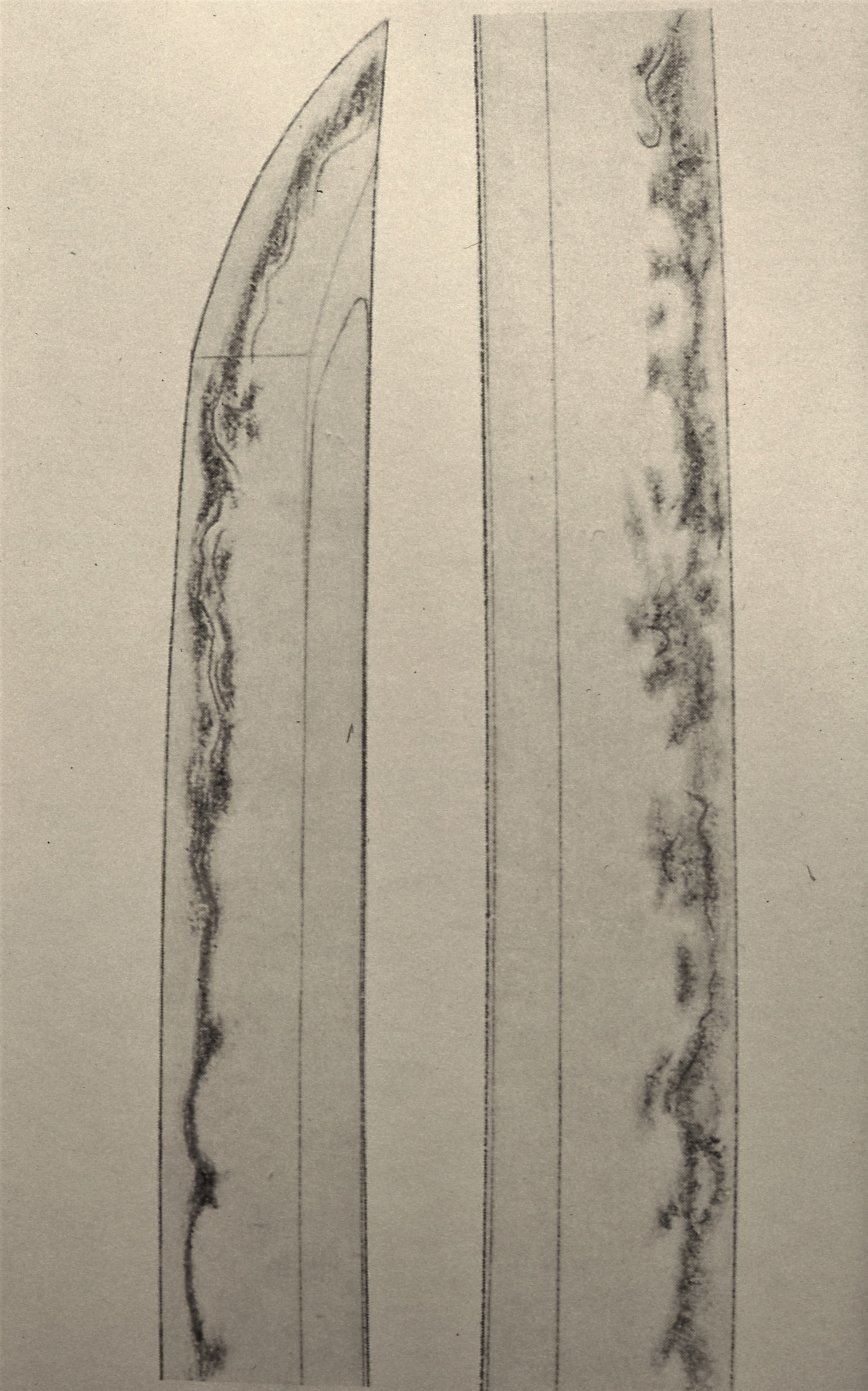
Enbun Joji Ko-wakizashi tanto is also called Sun-nobi tanto (>10 inches) because its length is longer than the standard size (about 10 inches) tanto. The upper part of the tanto curves outward slightly. This type is called sakizori.
Characteristics of Hiromitsu (広光) and Akihiro (秋広)
- Shape———————— Usually, one foot and one to two inches long (Sun-nobi). Wide width. Thin blade. Sakizori.
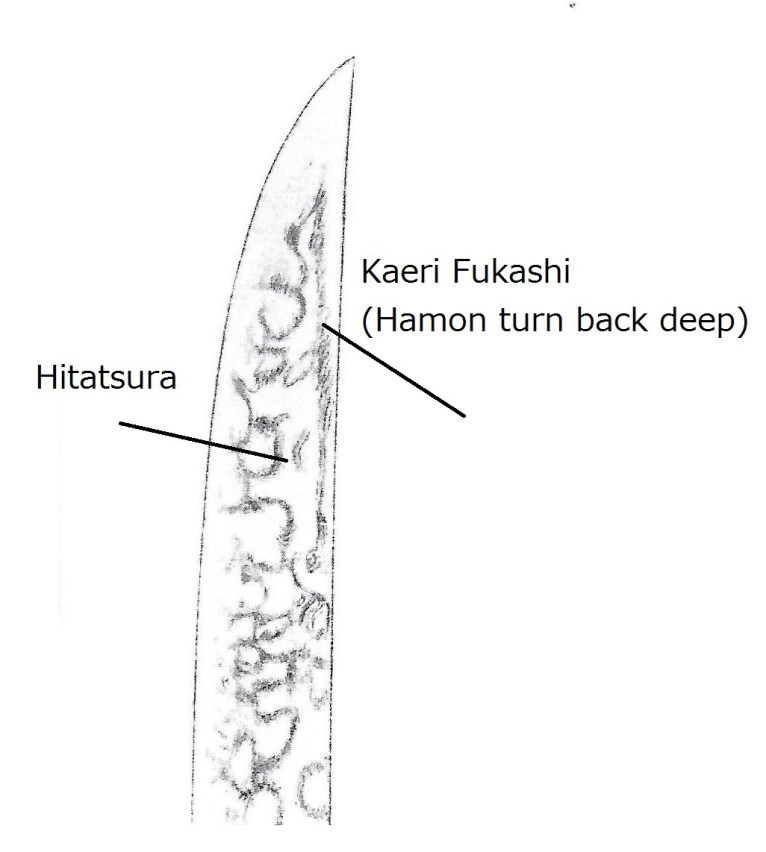
- Hamon ———————- A mix of wide and narrow hamon. The hamon around the yakidashi (just above the machi) area is narrow but gradually widens as it moves up. The hamon around the fukura area shows most work. Mainly nie. Sunagashi, kinsuji, gunome, umanoha-midare (horse teeth-shaped hamon), or hitatsura appear (drawing above).
- Boshi———-Irregular and unevenly tempered. The hamon covers almost the entire boshi. Deep turn back.
- Jihada ———————————————————Wood-grained pattern
- Nakago —————–Tanago-bara shape. Refer to 19 Nanboku-cho Period Tanto.
Nobukuni (Below is my sword)
Shodai Nobukuni (the first-generation Nobukuni) was a student of Sadamune. He was one of the Sadamune San Tetsu (貞宗三哲, Sadamune’s top three students). Nobukuni’s characteristics resembled those of Hiromitsu and Akihiro, as described above. Nobukuni also created sun-nobi tanto. The sword below has a hoso-suguha, ko-mokume (small burl pattern), and ko-maru boshi (small round).


 This is the certification of my sword. Shodai Nobukuni (初代信國). Juyo Token (重要刀剣)
This is the certification of my sword. Shodai Nobukuni (初代信國). Juyo Token (重要刀剣)
Certification
Number: Juyo 3220, Certification Juyo-Token
Wakizashi: Nobukuni (信国), 31.4cm long, 0.3cm curvature, hirazukuri, mitsumune (three-sided mune), sun-nobi. The ji-hada shows a wood grain and ji-nie (surface nie, between shinogi and hamon). The hamon is a chu-suguha (medium straight). The front carving shows bonji (Sanskrit) and sanko-ken. The back engraving is bonji and hoko (pike). Original nakago. Examined by the Nihon Bijutsu Token Hozon Kyokai. It is certified as a Juyo Token. The Chairman, Moritatu Hosokawa. Showa 45 June 1 (June 1, 1970)
 Masamune from Sano Museum Catalog (permission granted)
Masamune from Sano Museum Catalog (permission granted)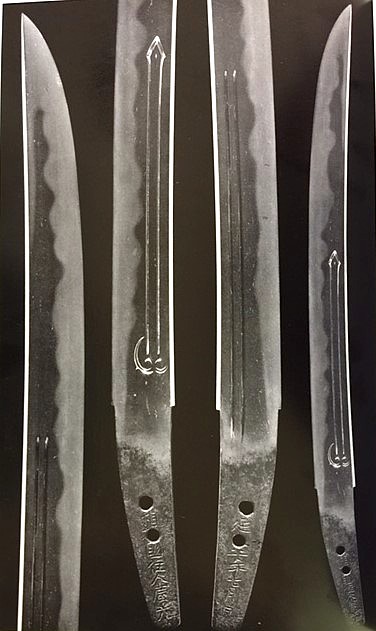
 Hiromitsu from Sano Museum Catalog (permission granted)
Hiromitsu from Sano Museum Catalog (permission granted)