
The circle indicates the time we discuss in this section
During the Nanboku-cho period, samurai sought large, elaborate, impressive, yet practical swords. The Soshu-den style sword from Nanboku-cho time was just that. This was the most popular style at the time. The Nanboku-cho period marked the peak and height of the Soshu-den sword. Many swordsmiths moved from other provinces to the Kamakura area and forged Soshu-den style swords. Other schools and provinces outside the Kamakura area also produced Soshu-den-style swords in their own areas.

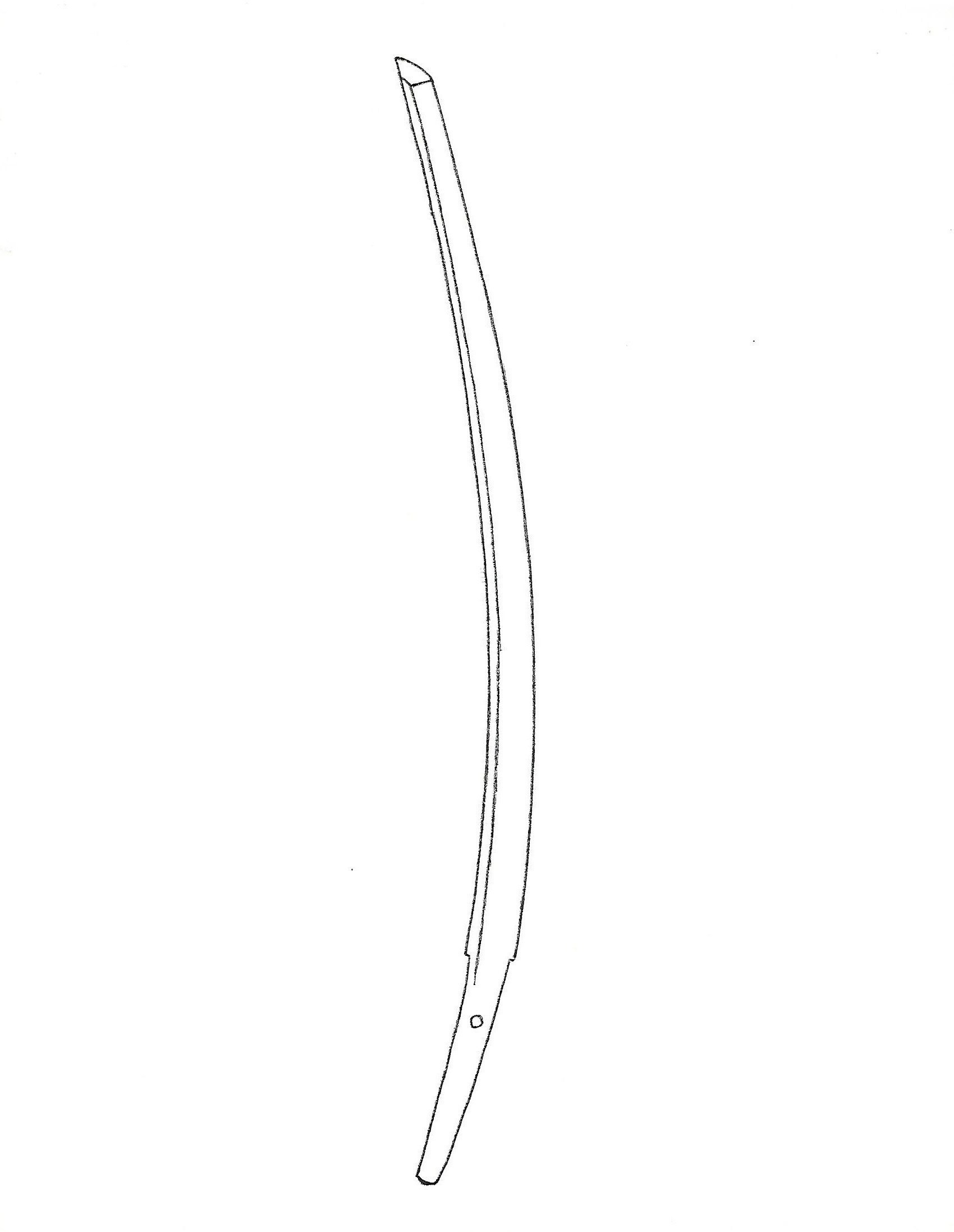
Sugata (姿: Shape) —————–The original length of a sword ranged from three to five feet, but it was later shortened to about two and a half feet. A significantly shortened blade is called o-suriage.
The Nanboku-cho style sword features shallow kyo-zori (also called torii-zori). Refer to Chapter 5, Heian Period Sword. The highest curvature occurs around the middle of the body. It has a wide body, high shinogi, narrow shinogi-ji (Chapter 3, Names of parts), and thin kasane (blade thickness), which are distinctive features of the Nanboku-cho style. High gyo-no-mune or shin-no-mune, and sometimes a maru-mune (round back).

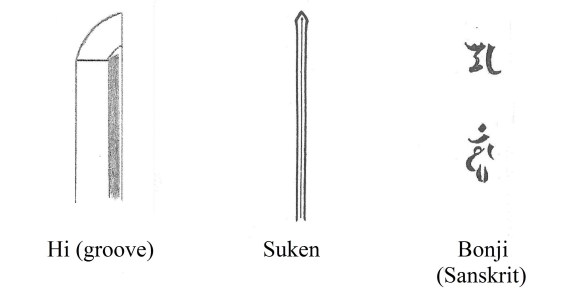
Hi (樋: groove) and Horimono (彫刻: engraving) ——– Often, a single hi (bo-hi), double hi, suken (dagger), Bonji (Sanskrit), and/or dragon are engraved on the shinogi-ji area. Refer to Chapter 3, Names of Parts.
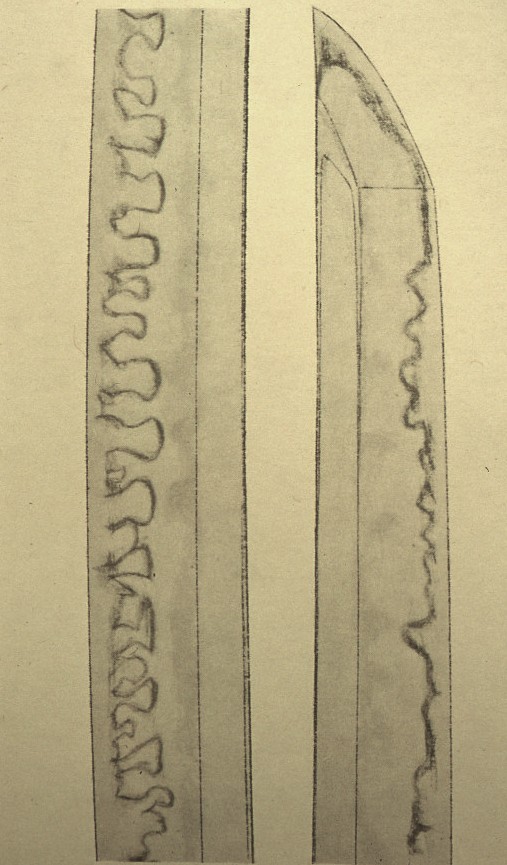
Hamon (刃: Tempered line) —- The lower part of the body exhibits a narrow-tempered line; gradually, this line becomes wider and showier. Course nie. O-midare (large, irregular, wavy hamon), Notare-midare (wavy, irregular hamon), and Gunome-midare (a combination of repeated half-circular and irregular hamon). Inazuma and kinsuji (see Chapter 14, Late Kamakura Period Sword) sometimes appear.



*From Sano Museum Catalogue ( Permission granted).
Ji-hada (地肌: the area between the shinogi and the tempered line) ———————-Wood-grain pattern (itame 板目). Sometimes tobiyaki (patchy tempered spots) appear on ji-hada. For ji-hada, refer to Chapter 3, Names of Parts.
Kissaki (切っ先) and Boshi (tempered line at the kissaki area) ———- O-kissaki (long and large kissaki). Fukura kareru (less arc kissaki). Midare-komi (the body and boshi have a similar tempered pattern), with kaeri-fukashi (hamon deeply turns back), and sometimes hitatsura (entirely tempered). See the illustration above.
Sword-smiths during Nanboku-Cho Period Soshu Den (school)
- From Soshu—————————————————Hiromitsu (広光) Akihiro (秋広)
- From Yamashiro ———————————————Hasebe Kunishige (長谷部国重)
- From Bizen (called So-den Bizen)——-Chogi (長儀 )group Kanemitsu (兼光 ) group
- From Chikuzen ———————————————————-Samoji (左文字 ) group
 Chogi (長義)from The Sano Museum catalog. Permission to use is granted
Chogi (長義)from The Sano Museum catalog. Permission to use is granted
The distinctive characteristics of the Nanboku-Cho period sword in the photo above
- The trace of an engraving of suken on the inside of the nakago indicates that this area was once a part of the main body.
- Large and long kissaki


 Kawazuko-choji O-choji Ko-choji Suguha-choji (tadpole head) (large clove) (small clove) (straight and clove)
Kawazuko-choji O-choji Ko-choji Suguha-choji (tadpole head) (large clove) (small clove) (straight and clove)
 Sansaku-boshi
Sansaku-boshi
 Osafune Nagamitsu(長船長光) From Sano Museum Catalogue (permission granted)
Osafune Nagamitsu(長船長光) From Sano Museum Catalogue (permission granted) 
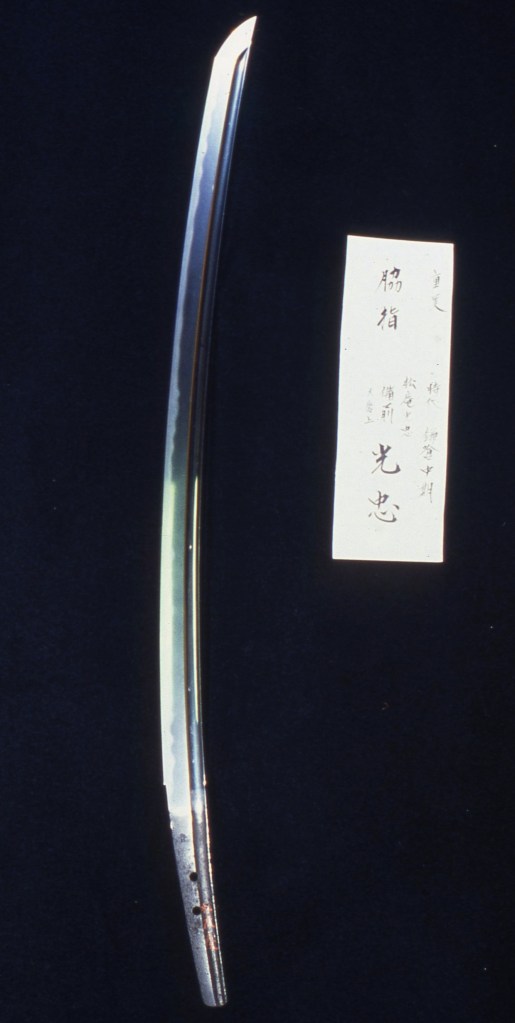 Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠) Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠)
Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠) Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠)