This chapter is a detailed part of Chapter 10, Jyokyu-no-Ran (承久の乱 ) 1221. Please read Chapter 10 before reading this section.

The red circle above indicates the time we discuss in this chapter.
Chapter 10 explained how Jokyu-no-ran (承久の乱) started. In the end, Emperor Gotoba (or Gotoba Joko) was exiled to Oki Island (隠岐の島).
Emperor Gotoba was a highly talented individual in many fields. He was good at waka (和歌), a Japanese short poem. To compose a waka requires including several elements, such as scenery, the season, personal feelings expressed with refined sentiment, or the surrounding environment, all within a very limited number of words. It requires literary talent. He was also proficient in equestrianism, kemari (a ball game played by the upper class at that time), swimming, sumo wrestling, music, archery, swordsmanship, calligraphy, painting, and even sword-making. His contributions to the sword field led to the golden age of sword-making during the middle Kamakura period. Surprisingly, Gotoba Joko was not only talented in many different arts but also mastered them at the highest level. His waka (poetry) was particularly highly regarded. He edited the Shin- Kokin- wakashu (新古今集), a collection of 1980 waka poems.
Emperor Gotoba, Enthroned at the Age Four
Emperor Gotoba was enthroned at the age of four (some say three). The problem was that Emperor Antoku was already on the throne. They were both about the same age. Having two emperors simultaneously creates a problem. How did this happen?
To establish a new emperor, the head of the imperial family must appoint the next emperor. While Emperor Go-Shirakawa (後白河天皇) was imprisoned, Emperor Antoku was appointed by Taira-no-Kiyomori (平清盛). Although Kiyomori was the head of the Heishi, the most powerful samurai group, he was not a member of the imperial family. That went against tradition. This was unacceptable to Emperor Go-Shirakawa (後白河天皇). Emperor Go-Shirakawa was furious at Taira-no-Kiyomori; he chose Emperor Gotoba and enthroned him. This is why the two emperors coexisted.
There was one more thing. To be an emperor, one must possess the Sanshu-no-jingi (三種の神器: Three imperial regalia). These are the three items an emperor needs to have to be a legitimate emperor. They are a mirror, a sacred sword, and a magatama (jewelry)*.
However, the Sanshu-no-jingi were taken by the Heike family along with Emperor Antoku when they fled from the Genji. The Heike clan was chased by the Genji all the way to Dan-no-ura (壇ノ浦), where they were defeated. Dan-no-ura is a sea located between Kyushu (九州) and Honshu (本州). When it became clear to the Heike family that they had been defeated, all of the Heike people, including the young Emperor Antoku, jumped into the sea and drowned. They took the Sanshu-no-jingi with them into the sea.
Later, people frantically searched for the Sanshu-no-jingi; however, they only recovered the jewelry and the mirror, not the sword. Because of tradition, the emperor must possess the Sanshu-no-jingi; otherwise, he would not be recognized as a legitimate emperor. Gotoba Joko was tormented for a long time for not having all three.
Today, the jewelry is with the current emperor’s family, and the mirror is at the Ise Jingu Shrine (伊勢神宮). The sword is still missing somewhere in the ocean. Some say that the sword that fell into the sea was a replica, and the one kept at Atsuta Jingu Shrine (熱田神宮) is the real one. * Sanshu-no-Jingi (三種の神器) ————- 1. The sword; Kusanagi-no-tsurugi (草薙の剣) 2. The mirror; Yata-no-kagami (八咫の鏡), 3. The magatama (Jewelry); Yasakani-no-magatama (八尺瓊勾玉) by Token World: www.touken-world.jp/tips/32747/
Politics by Emperor Gotoba
Emperor Gotoba sought to regain political power from the Kamakura bakufu. He was impulsive, passionate, unpredictable, and quick-tempered. He tried to revive the Chotei (朝廷) power. The Chotei is the central government controlled by the emperor and aristocrats. Emperor Gotoba decided to rely on the armed forces to achieve this goal and established the Saimen no Bushi (armed forces directly under the emperor).
Upon seeing Minamoto-no-Sanetomo dead, he realized that the Kamakura bakufu was in turmoil. Recognizing this as a good chance, he sent out the emperor’s order to all the daimyo to fight against the Kamakura bakufu. He expected an easy victory, but the Kamakura bushi remained strongly united and fought well under Hojo Masako’s leadership, the “Nun Shogun.” She organized a strongly united armed force, while Emperor Gotoba’s side was disorganized. They were not accustomed to fighting.
In the end, Emperor Gotoba’s side lost. When he realized he had lost, he claimed it was not he but his men who had acted independently. He insisted that it had nothing to do with him. Therefore, it was wrong to punish him. But of course, Hojo Masako and the Kamakura bakufu did not believe Emperor Gotoba and exiled him to Oki Island. Emperor Gotoba ended his life there. Although he was intelligent and accomplished in many areas, he could not defeat the grandma, “Nun Shogun,” Hojo Masako.
Sword-Making by Gotoba Joko
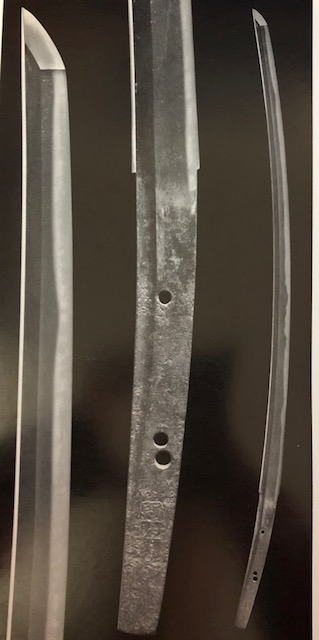
Gotoba Joko had an exceptional ability to evaluate swords, and he became a great swordsmith himself. He invited many top-level swordsmiths from various groups to his court, gave them titles, and treated them with respect. He also appointed them as his instructors and assistants. Gotoba Joko brought in skilled swordsmiths from various places in rotation. Those who were invited to the palace were called gobankaji (御番鍛冶), an honorary title. On the sword he created, he inscribed a chrysanthemum with 16 petals. The current emperor still uses this design as his imperial crest. The sword with the chrysanthemum design is called Kikugosaku (菊御作).
Today, you can visit the Emperor Gotoba Museum on Oki Island, where some sites are believed to be the emperor’s sword-making site. Some people say it is debatable whether these sites are real. Today, Oki Island is a beautiful resort destination. It can be reached by ferry from Shimane Prefecture, which takes about two hours. It can also be reached by airplane directly from Osaka.

Gotoba Joko, owned by Minase Shrine (This picture is in the public domain)