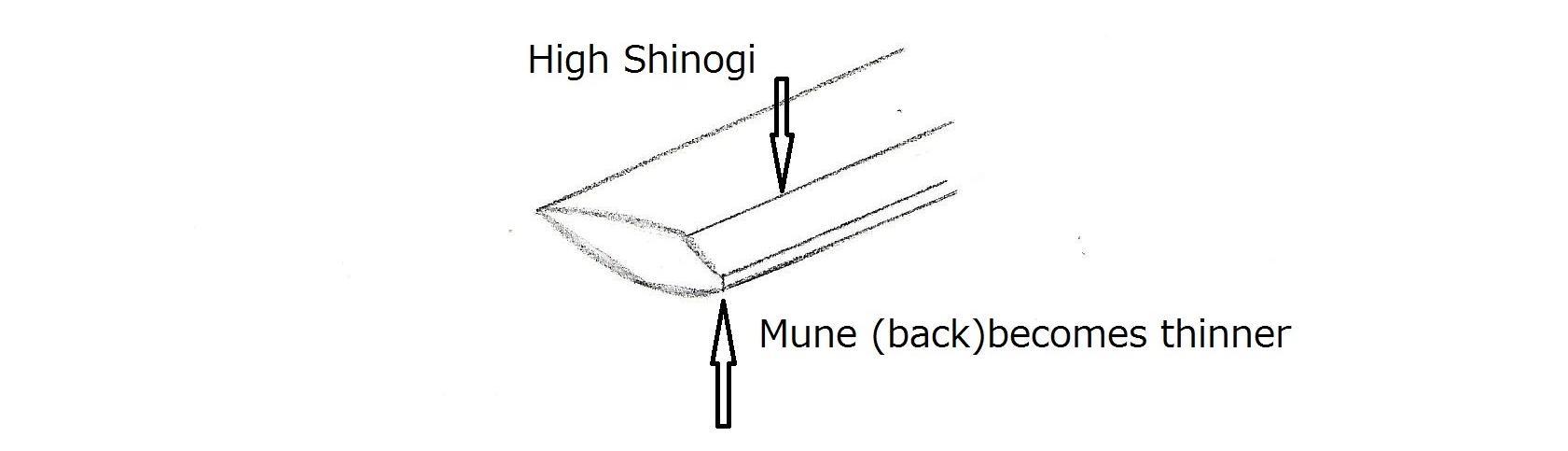
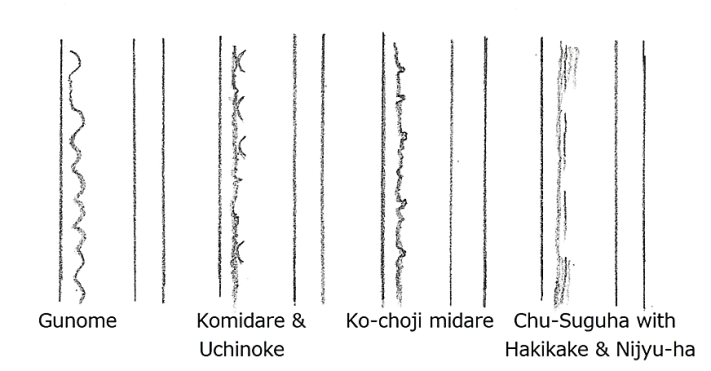
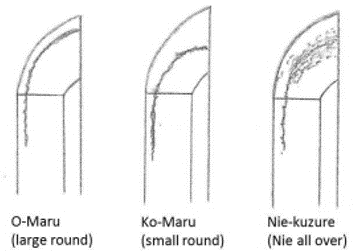
This chapter is a detailed part of Chapter 28, Shin-t Main 7 Regions (part B). Please read Chapter 28 before reading this chapter. Below are regions 3 and 7.
 The red circle above indicates the time we discuss in this section
The red circle above indicates the time we discuss in this section
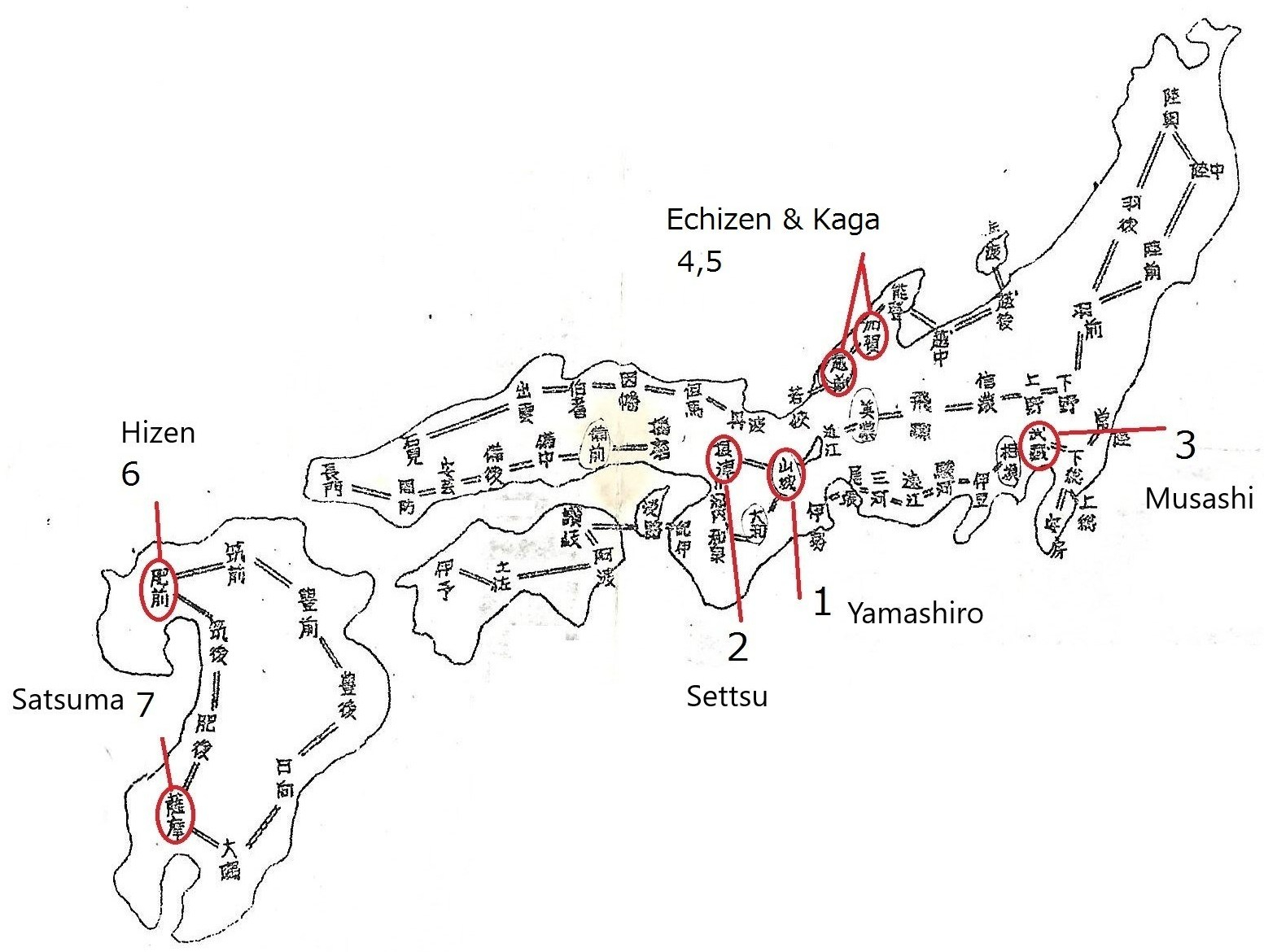
3.Musashi (Edo)
We also find many famous swordsmiths in Edo. They were Yasutsugu (康継), Kotetsu (虎徹), Noda Hankei (野田繁慶), Hojoji Masahiro (法成寺正弘), and their followers.
Two photos below are swordsmiths from Musashi (武蔵: Tokyo).
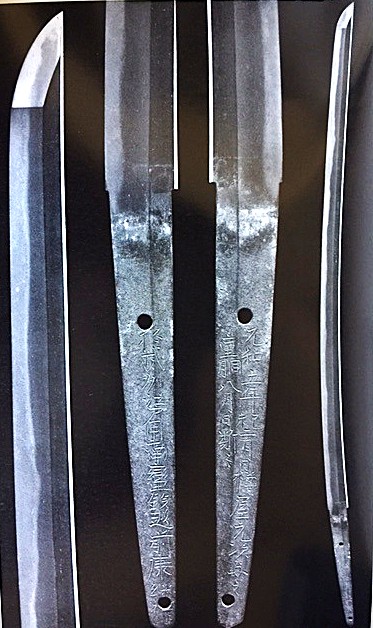
 Yasutsugu From the Sano Museum Catalogue. (Permission to use granted)
Yasutsugu From the Sano Museum Catalogue. (Permission to use granted)
Characteristics of Yasutusgu (康継) ——Shallow curvature; chu-gissaki (medium kissaki); a wide notare hamon, midare, or o-gunome (occasionally double gunome); traces of Soshu-den and Mino-den; a wood-grain pattern mixed with masame on the shinogi-ji.

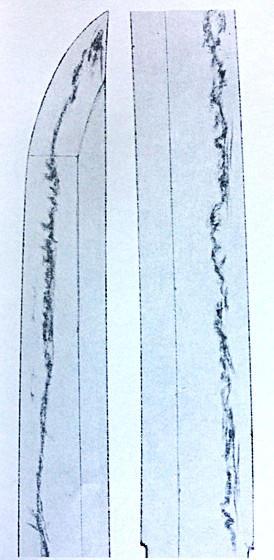
 Kotetsu (虎徹) from Sano Museum Catalogue, (permission to use granted)
Kotetsu (虎徹) from Sano Museum Catalogue, (permission to use granted)
Here is the famous Kotetsu. His formal name was Nagasone Okisato Nyudo Kotetsu (長曽祢興里入道虎徹). Kotetsu started making swords after turning 50. Before that, he was an armor maker.
The characteristics of Kotetsu ———————— A shallow curvature and wide width, a wide tempered line with nie. A small irregular hamon surrounds the machi area, transitioning into a wide suguha-like notare in the upper area. Fine nie, komaru–boshi with a short turn back. The ji-hada is a fine-grained wood with burl. Occasionally, o-hada (black core iron shows through) appears in the lower part above the machi area. The illustration above shows a thick-tempered line with nie, a typical feature of Kotetsu. Once you see it, you will remember it. The next region is 7 (skip 4, 5, and 6)
- Satsuma (Kyushu)

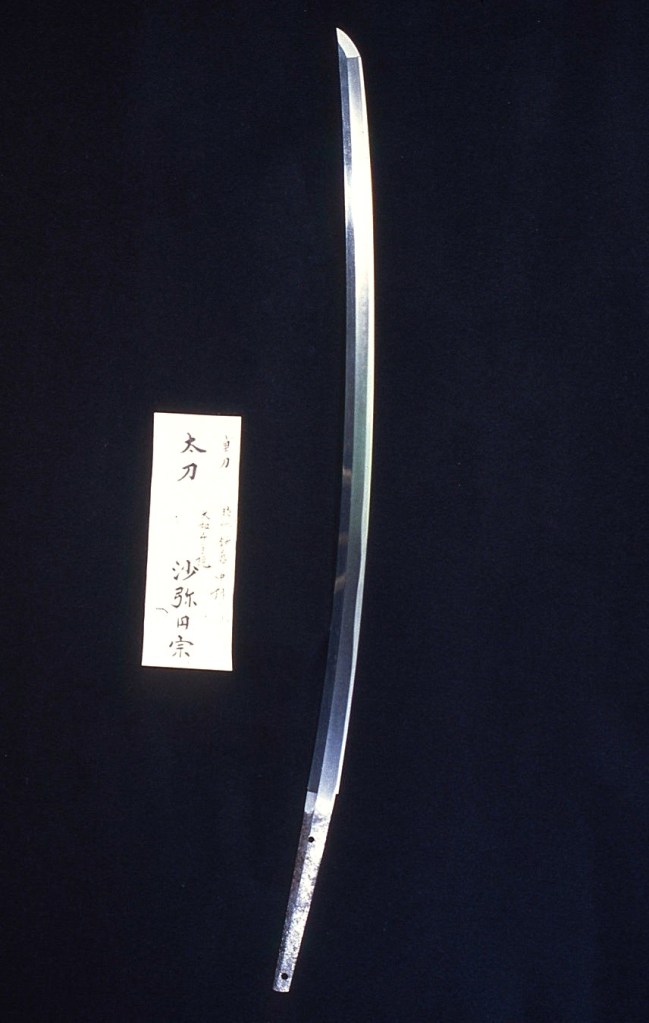
 Miyahara Mondonosho Masakiyo (宮原主水正正清) from Sano Museum Catalogue (permission to use granted).
Miyahara Mondonosho Masakiyo (宮原主水正正清) from Sano Museum Catalogue (permission to use granted).
Miyahara Mondonosho Masakiyo was highly respected by the Shimazu family of Satsuma- han (the Satsuma domain in Kyushu). Later, he was chosen to travel to Edo to forge swords for Shogun Yoshimune.
Mondonosho Masakiyo’s characteristics————- Well-balanced sword shape, shallow curvature, and wide and narrow hamon mixed with squarish hamon and pointed hamon as shown in the photo above. He engraved the Tokugawa family’s Aoi crest (the hollyhock crest) on the nakago.