This is a detailed section of Chapter 14| Late Kamakura Period Sword. Please read Chapter 14 before this part.

The red circle above indicates the time we discuss in this section.

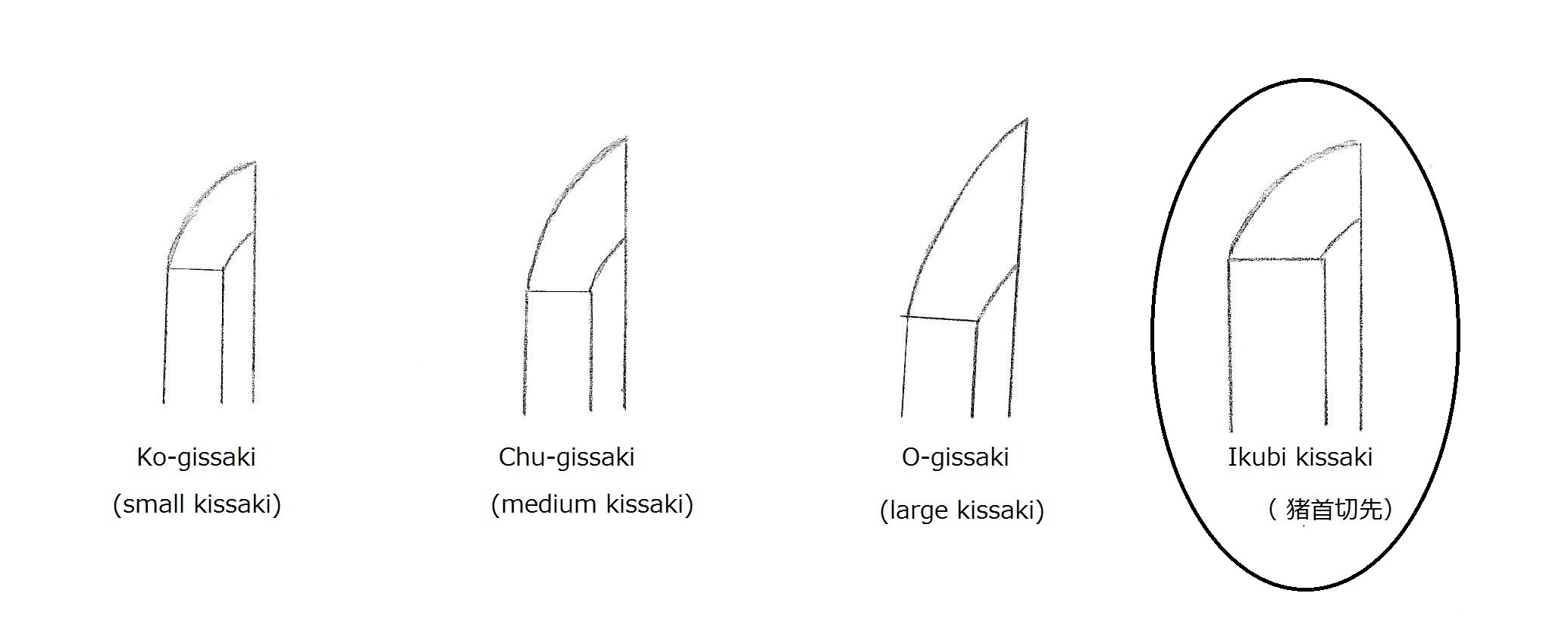
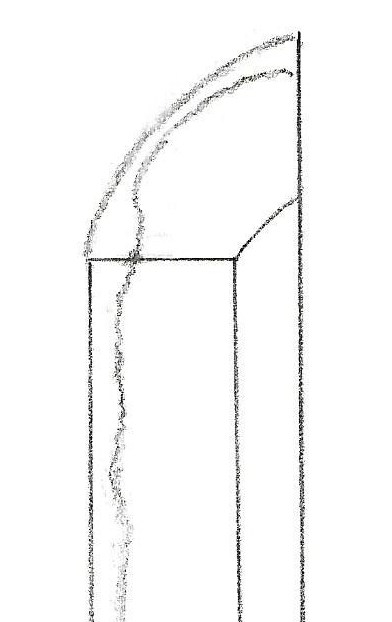
In Chapter 14, “Late Kamakura Period Sword (鎌倉末太刀),” the ikubi-kissaki sword is explained. The illustration above shows a flaw caused when the damaged area was repaired. To compensate for this flaw, swordsmiths developed a new sword style during the late Kamakura period. They forged swords with a longer kissaki and lowered the tip of the hi below the yokote line. This way, if the yokote line were lowered during repairs, the tip of the hi would remain below the yokote line.

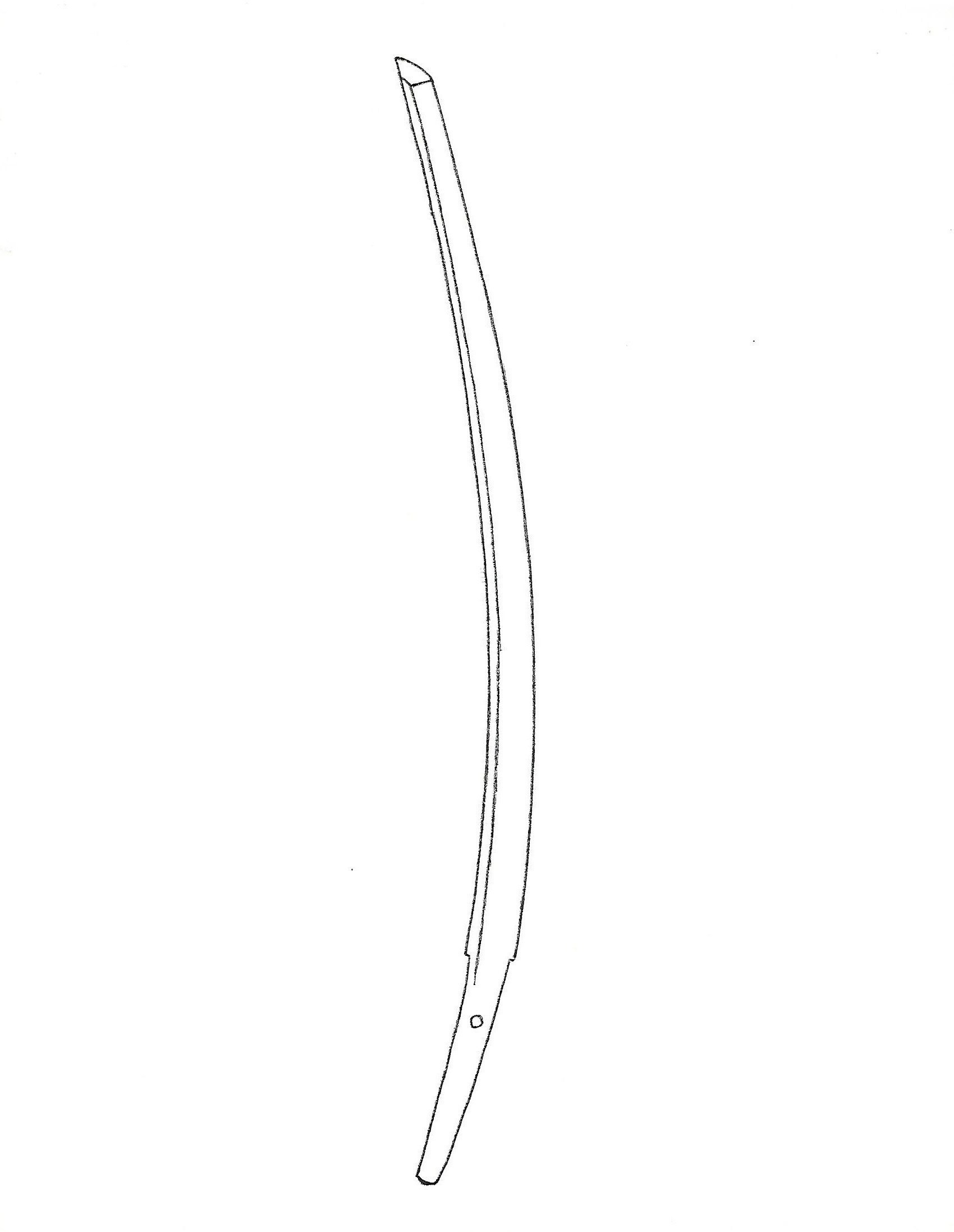
The above photo shows a sword by Goro Nyudo Masamune (五郎入道正宗). Please observe the size and shape of the kissaki. This differs from the previous ikubi-kissaki and ko-gissaki styles. This style represents a typical late Kamakura period kissaki style. It is o-suriage (a largely shortened form).
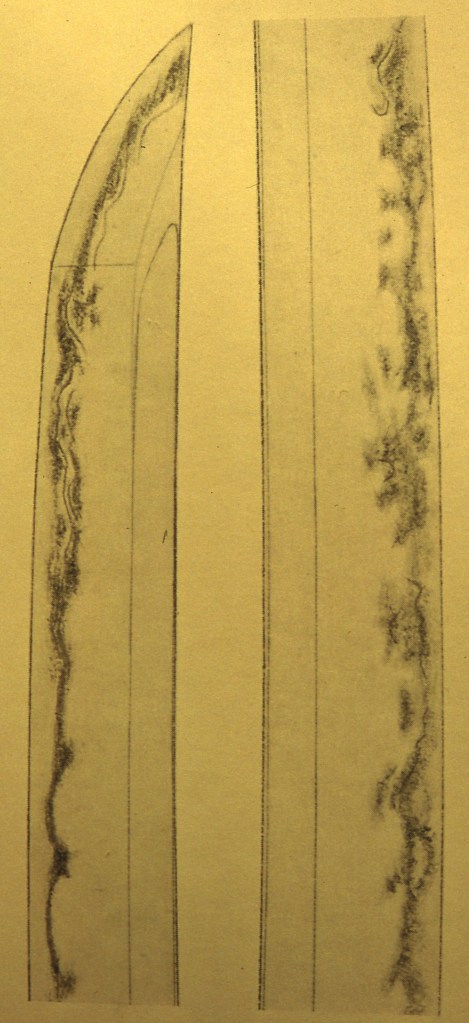
Under the Kamakura Bakufu, many swordsmiths moved to Kamakura. They were Toroku Sakon Kunituna (藤六左近国綱) of the Yamashiro Awataguchi group (山城粟田口), Fukuoka Ichimonji Sukezane (福岡一文字助真), and Kunimune (国宗) from the Bizen area. They were the origin of Soshu-den (相州伝). Eventually, Tosaburo Yukimitsu (藤三郎行光) and his famous son, Masamune (正宗), emerged. In the drawing above, kinsuji and inazuma are shown within the hamon. The shining lines inside the hamon are inazuma and kinsuji. Inazuma and kinsuji are collections of nie. Masamune is well-known for his inazuma and kinsuji. He lived in Kamakura, a seaside town, and his hamon resembles ocean waves when viewed from the side.


The picture above shows a sword made by the swordsmith Yoshioka Ichimonji group (吉岡一文字). The kissaki resembles one of Masamune’s swords. It is longer than the previous ikubi-kissaki or ko-gissaki. This is chu-gissaki. The kissaki, like this, is one of the key points in determining the period when the sword was made. The hamon has choji, gunome, togariba (pointed tip), and very tight nie.

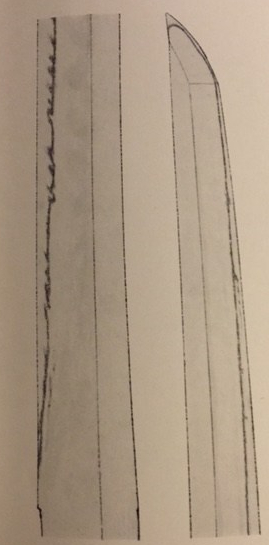
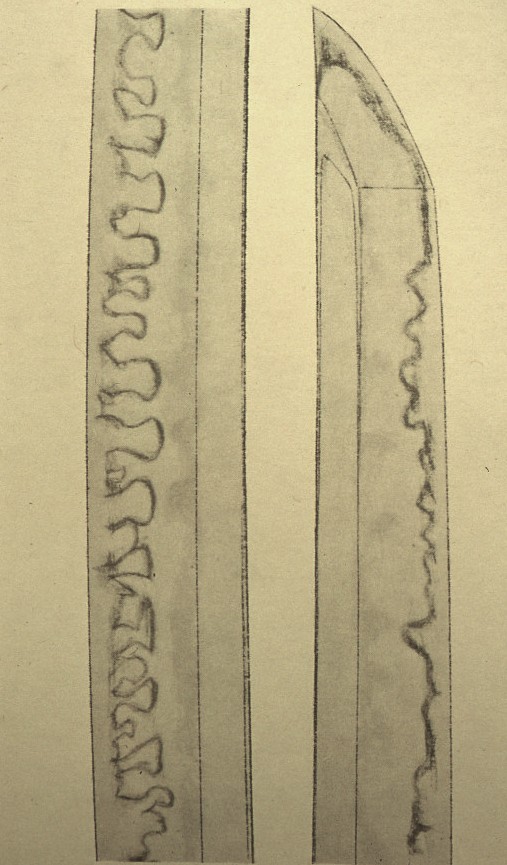
The photo above shows a sword by Ukai Unsho (鵜飼雲生) from Bizen-den. This sword is also from the late Kamakura period, but it has a ko-gissaki. This sword does not have the late Kamakura period chu-gissaki style. Narrow hoso-suguha are more characteristic of an earlier time than the late Kamakura period. This sword indicates that swords do not always exhibit the style of their period. To kantei*: first examine the style and shape, then give yourself an idea of the period it was made in. However, the kissaki in this case does not indicate the late Kamakura period. The next step is to look at the various characteristics of the sword one by one, such as the hamon, nie or nioi, ji-hada, etc., to determine the period, the den, and the province, and then come up with the name. This process is called kantei.
*Kantei – the process of identifying a swordsmith’s name by analyzing the sword’s characteristics without seeing the mei (the inscribed smith’s name). The mei might be gone if it has been shortened. All the photos above are from the Sano Museum Catalogue. Permission to use them is granted.







 Kawazuko-choji O-choji Ko-choji Suguha-choji (tadpole head) (large clove) (small clove) (straight and clove)
Kawazuko-choji O-choji Ko-choji Suguha-choji (tadpole head) (large clove) (small clove) (straight and clove)
 Sansaku-boshi
Sansaku-boshi
 Osafune Nagamitsu(長船長光) From Sano Museum Catalogue (permission granted)
Osafune Nagamitsu(長船長光) From Sano Museum Catalogue (permission granted) 
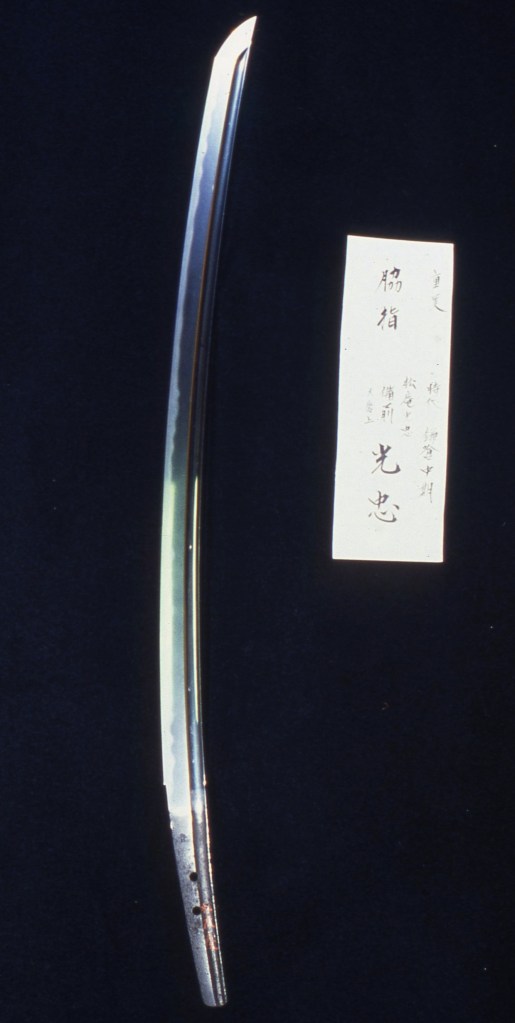 Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠) Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠)
Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠) Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠)