The red circle indicates the subject of this chapter
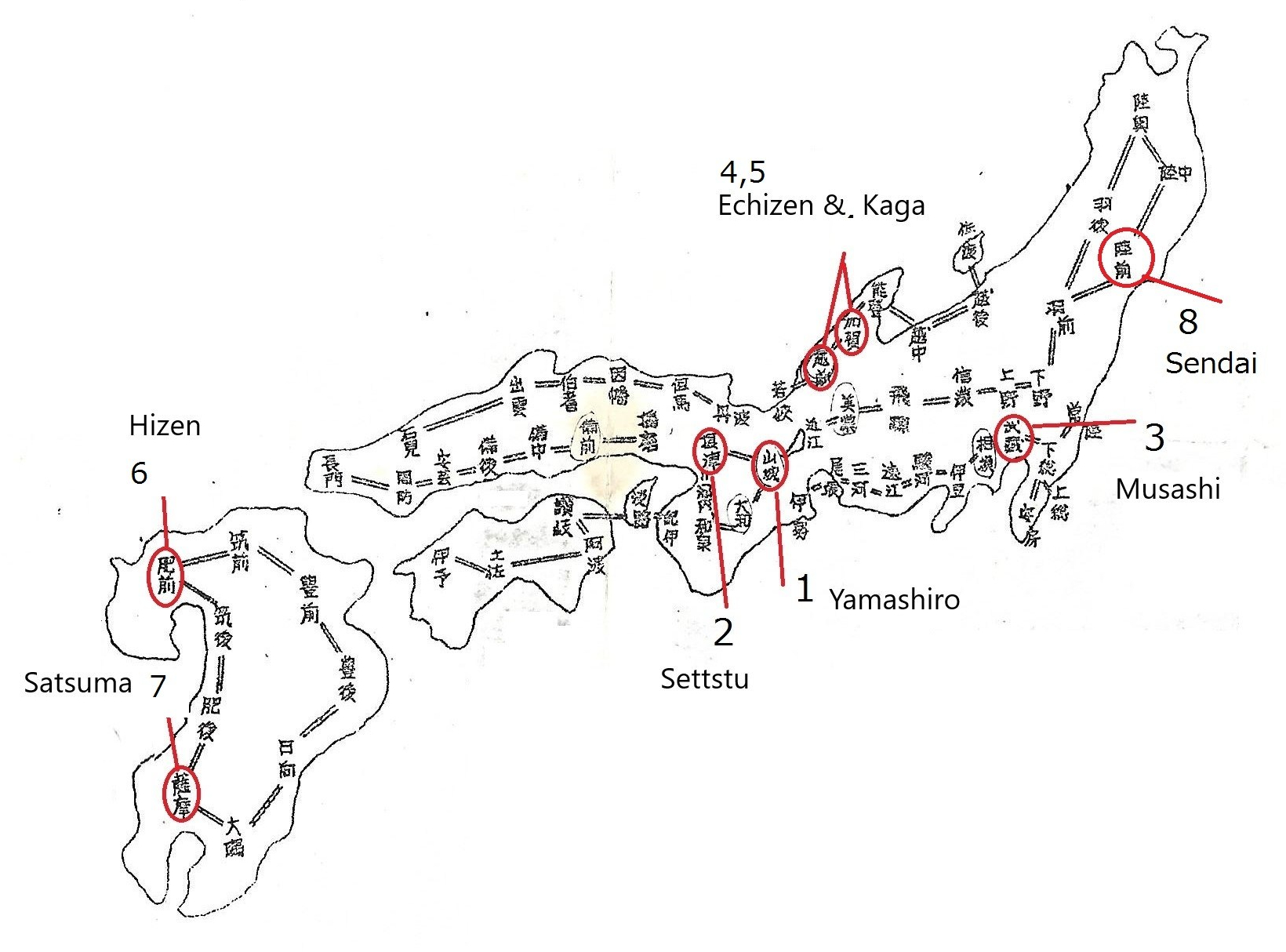
3.Musashi ( 武蔵 ) in Edo ( 江戸 )
The katana and wakizashi made in the Musashi area have a shallow sori (curvature). Often, the width of the blade’s upper part is narrow. Usually, the hamon begins with a slight irregular pattern, then gradually shifts to a larger irregular pattern, and a few inches below the yokote line, it becomes a small irregular pattern again. The boshi is usually a komaru-boshi. The ji-hada may be rough. Masame-hada shows on shinogi-ji.
Well-known swordsmiths in Musashi ———————————-Noda Hannkei (野田繁慶) Nagasone Okisato Nyudo Kotetsu (長曽根興里入道虎徹)

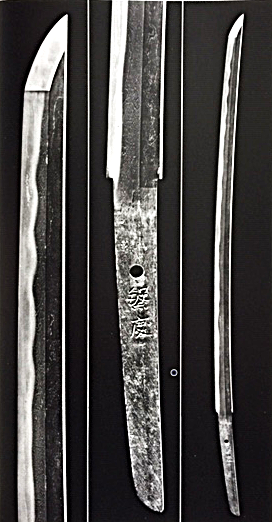
Nagasone Okisato Nyudo Kotetsu Noda Hankei (野田繫慶) (長曽根興里入道虎徹) from Compton’s collection “Nippon-to” Once, my family sword
4. Echizen ( 越前 ) and 5. Kaga (加賀 )
Many swordsmiths from the Mino (美濃) area moved to the Echizen and Kaga areas (#4 & #5 on the map above). Therefore, swords made in these areas are called Echizen-seki and Kaga-seki. Refer to Chapter 23 Sengoku Period (戦国) Sword for Mino-den. The style of Echizen Yasutsugu (越前康継) is similar to that of Mino-den.
Well-known swordsmith in Echizen ————————-—Echizen Yasutsugu (越前康継 )
6. Hizen (肥前)
Both the katana and wakizashi from Hizen have well-balanced shapes. The Hizen region tends to produce swords with a chu-suguha-hotsure (a medium-width straight hamon resembling frayed fabric) with fine nie (沸). The boshi has a clean, regular line with a uniform width tempered line, as shown in the illustration below. If you see a shin-to sword that has a chu-suguha hamon and a boshi that looks like the one below, it is often made by Hizen Tadayoshi (肥前忠吉). Very fine Ji-hada (surface), sometimes called nukame-hada.

Well-known swordsmith in Hizen ——————————— Hizen Tadayoshi ( 肥前忠吉)
- Satsuma (薩摩 )
The swords made in Satsuma appear solid for both katana and wakizashi. The kissaki (the top pointed area) is slightly stretched. Yakidashi (a few inches above the machi ) shows a small, irregular hamon. The hamon is o-midare with coarse nie called ara-nie. The ara-nie forms togari-ba (a pointed pattern; see the drawing below). One of the characteristics of this region.
The region is well known for its Satsuma-nie. That is, the ara-nie around the hamon continues and blends into the ji-hada area. Therefore, the border between ha-nie and ji-nie is unclear. Inside the hamon, it sometimes shows a thick line shaped like lightning. This line is called Satsuma-no-imozuru (sweet potato vine), and is less desirable than inazume and kinsiji. This is the most prominent feature of the Satsuma sword. Boshi has a narrow-tempered line with a small irregular pattern. This is called satsuma-boshi. On the ji-hada surface, chikei (a long, dark line) appears. This is called Satsuma-gane (薩摩金).

Well-known swordsmiths in Satsuma —————— Izunokami Masafusa (伊豆守正房) Ichinohira Yasuyo (一平安代) Mondonosho Masakiyo (主水正正清)
