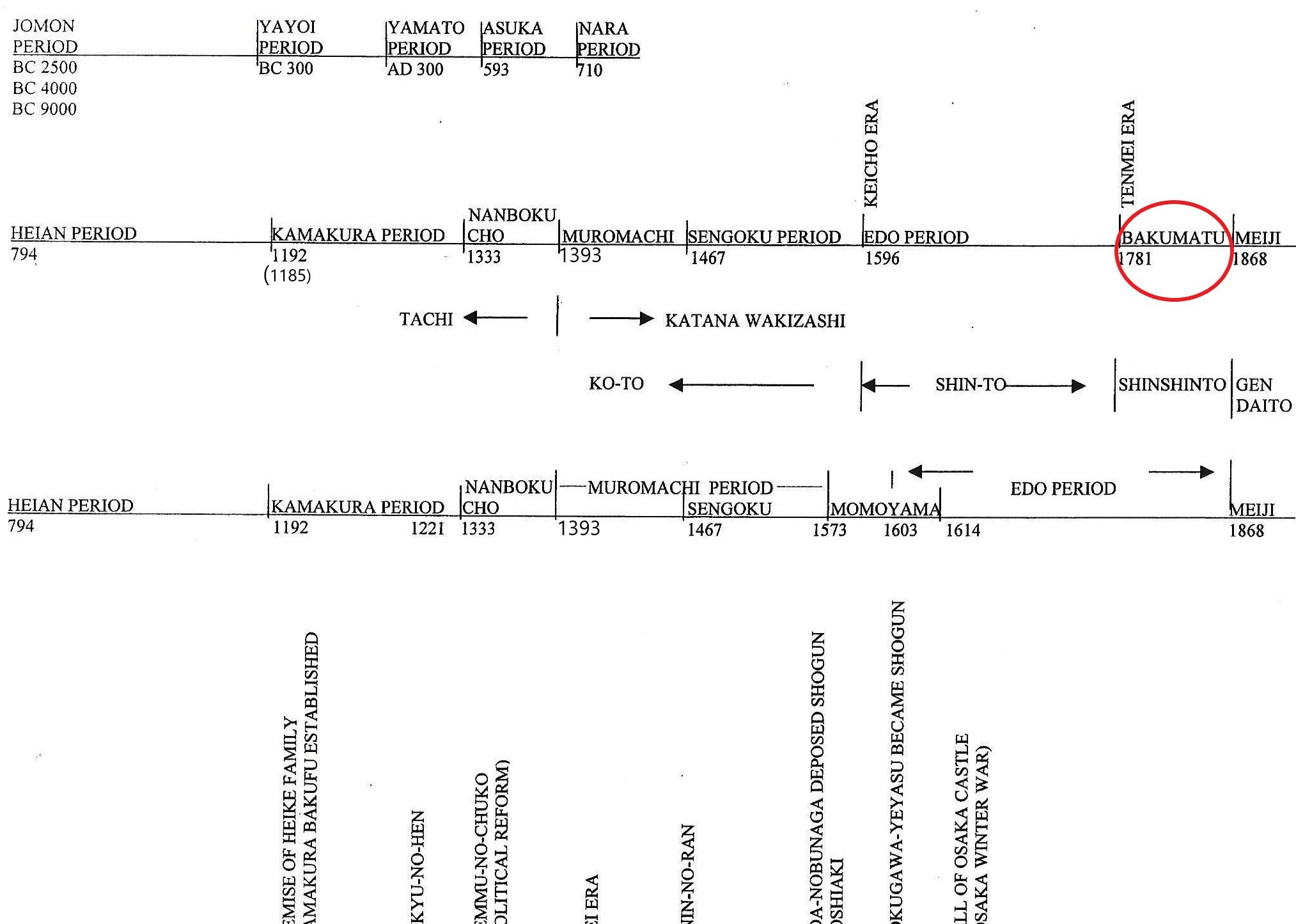
The circle above indicates where we discuss in this chapter.
Between the Sengoku period (戦国時代) and the Edo period (江戸時代) in Japanese political history, there was a time called the Azuchi-Momoyama period (安土桃山). It lasted from around 1573 to 1614, as shown in the third (bottom) timeline above. This was the era when Oda Nobunaga (織田信長), Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣秀吉), and Tokugawa Ieyasu (徳川家康) played central roles in politics.
After Tokugawa Ieyasu (徳川家康) won the Battle of Sekigahara (関ヶ原の戦い) in 1600 and defeated Toyotomi’s vassals (Toyotomi Hideyoshi had already passed away by then), Tokugawa Iyeyasu became the shogun (将軍) in 1603. This marked the start of the Edo Period (江戸). In sword history, as shown in the middle timeline above, the Edo period follows immediately after the Sengoku period.
At the end of the Sengoku period and throughout the Azuchi-Momoyama period, the economy grew significantly, and new cultures flourished. Beautiful and impressive art forms, such as paintings, architecture, and interior design, were created. The tea ceremony was developed by Sen No Rikyu (千の利休), and Kabuki began to be performed during this period. This era was somewhat similar to the European Renaissance. Interestingly, this emergence occurred in Japan and Europe around the same time.
Around this time, many Europeans came to Japan. That was during the era of European exploration in the East. They were from England, Spain, Holland, and Portugal. The novel “Shogun” by James Clavell is based on the true stories of William Adams and Jan Joosten Van Londersteyn*¹ from that period. Today, you can see Jan Joosten’s statue at Tokyo Station. I stay at a hotel near Tokyo Station on my yearly trip to Japan. I often pass by in front of “Jan Joosten’s” statue. It is located underground inside Tokyo Station, right in the busy shopping area. It can be easily missed unless you look for it. There is also another statue of him outside the station.
Shogun Tokugawa Iyeyasu hired William Adams and Jan Joosten (the Japanese call him Jan Joosten, not his full name) as his advisors, and he gained information about Europe from them. Shogun Tokugawa Iyeyasu treated them well. The area where Jan Joosten lived is now called Yaesu (八重洲), named after him. William Adams changed his name to Miura Anjin and lived in the Miura area. This place is about an hour and a half south of Tokyo today. The records of these two men are well-kept and easily accessible.
Europeans introduced many European goods and ideas to Japan. Although Christianity became popular and spread widely during the early Azuchi-Momoyama period, Toyotomi Hideyoshi later banned it. After the Meiji Era (1868), religious restrictions were lifted.
The Edo period started when Tokugawa Iyeyasu became shogun (1603) and ended with the Meiji (明治) Restoration in 1868. The Tokugawa bakufu, or Tokugawa government, was the sole governing entity in the country during this period. Although emperors still existed, political power shifted to the Tokugawa bakufu.
Gradually, ports for European ships were restricted. Eventually, Spaniards were no longer allowed to come to Japan, and then the Portuguese. The Japanese were also banned from traveling abroad. By around 1640, Dejima, a port town in Hirato, Nagasaki Prefecture, was the only place in Japan where foreigners could do business with the Japanese. Only the Dutch were allowed to arrive from Europe. Japan isolated itself from the outside world until the Meiji Restoration (1868).
During the Azuchi-Momoyama and early Edo periods, many European ships visited Japan. Strangely, a lot of these ships wrecked near Japan’s shores. One reason is that Japan is a volcanic island. Even if the sea’s surface appears calm, there are many obstacles beneath the surface, such as underwater mountains and large hidden reefs. The Europeans lacked the waterway information common among Japanese seamen.
Additional stories to share just for fun
Another reason many ships were wrecked was that they were searching for gold. When Marco Polo traveled to China, he heard from the Chinese people about a small island country farther to the east. This land was prosperous, and the emperor’s palace was made of gold and silver. After Marco Polo returned to Italy, he published a book (in the late 1300s) about his journey. In his book, he mentioned what he had heard about the island nation of Japan in China, even though he had never visited Japan himself. The book was widely read across many European countries. Once traveling to the East became possible for Europeans, they came to Japan in search of gold.
Yes, Japan produced a large amount of gold. However, for the Europeans, it was too late. By then, the Fujiwara family had already mined most of the gold in the Oh-shu area (奥州, northern Japan). This area includes the present-day prefectures of Aomori, Akita, Fukushima, and Miyagi, where the devastating tsunami hit in 2011. Toyotomi Hideyoshi also owned many gold mines, but they had already been mined as much as possible with the skills available at that time. Japan once had many gold and silver mines across the country. Those mines are now depleted, and only a few remain available for mining today.
Throughout history, there have been facts and rumors about “maizo-kin: 埋蔵金.” Maizo-kin refers to gold buried or hidden by people such as the Tokugawa Shogun, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, wealthy daimyo, and merchants. Without vaults, the only way to store gold was to bury it in secret places. Several maizo-kins have been discovered, including one in the middle of Tokyo, Ginza. There are still several large ones that haven’t been found yet. These include Hideyoshi’s maizo-kin, the Tokugawa bakufu maizo-kin, and several others. Although several maps indicated the locations of these maizo-kin, they were, of course, fake. Today, whenever the ground is dug up to build a large structure, people start discussing the discovery of a big maizo-kin.
Gold gradually flowed out of Japan over the centuries until the Meiji Restoration, because the exchange rate between gold and silver was much cheaper in Japan than elsewhere. Today, we still mine gold on a small scale.
It is said that the name of the country, Japan, originates from Marco Polo’s book. He referred to Japan as “Chipangu,” which means “gold country,” in his book. *² From “Chipangu” to “Zipang” to ‘Jipang,” it eventually became “Japan.” The Japanese don’t call the country Japan but “Nihon” or “Nippon” (日本).
*¹ヤン ヨーステン 【Jan Joosten van Lodenstijn 】https://www.weblio.jp Or Jan Joosten van Londensteyn
*² Wikipedia “Names of Japan” or Check (Click) right to go to the link Jipangu
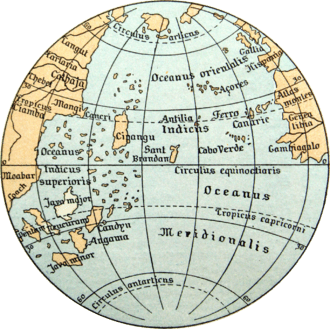
Cipangu was described in 1492 by Martin Beham’s globe From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository (Names of Japan)