This chapter is a detailed part of Chapter 8| Middle Kamakura Period –Yamashiro Den(鎌倉中期山城伝). Please read Chapter 8 before reading this chapter.

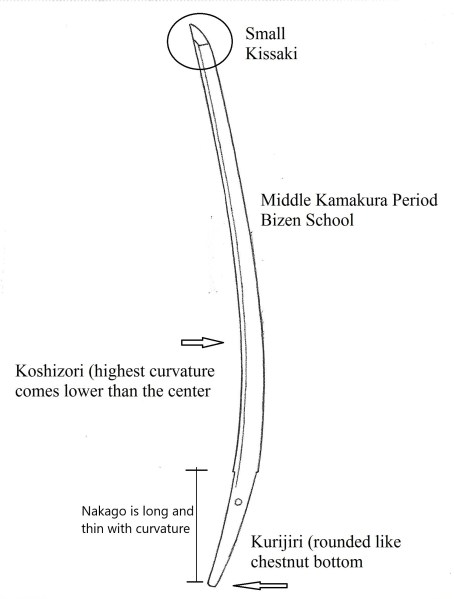
The red circle indicates the time we discuss in this section
During the middle Kamakura period, the Yamashiro–den consisted of 3 main groups: the Ayano-koji (綾小路) group, the Awataguchi (粟田口) group, and the Rai (来) group.
When referring to a specific group, we use terms like “xxx ha,” “xxx ippa,” or “xxx ichimon.” We use these three terms interchangeably. They all mean “group.” For example, when we say “Ayano-koji ippa,” we refer to the Ayano-koji group.
Ayano-koji Ippa (綾小路)
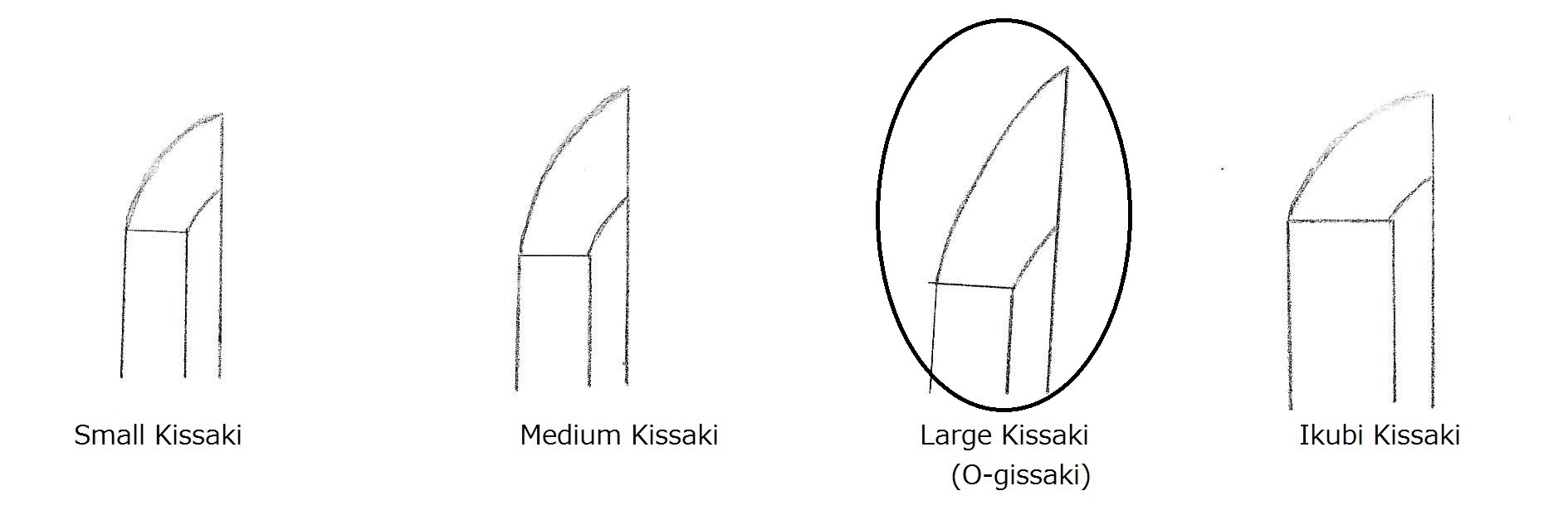
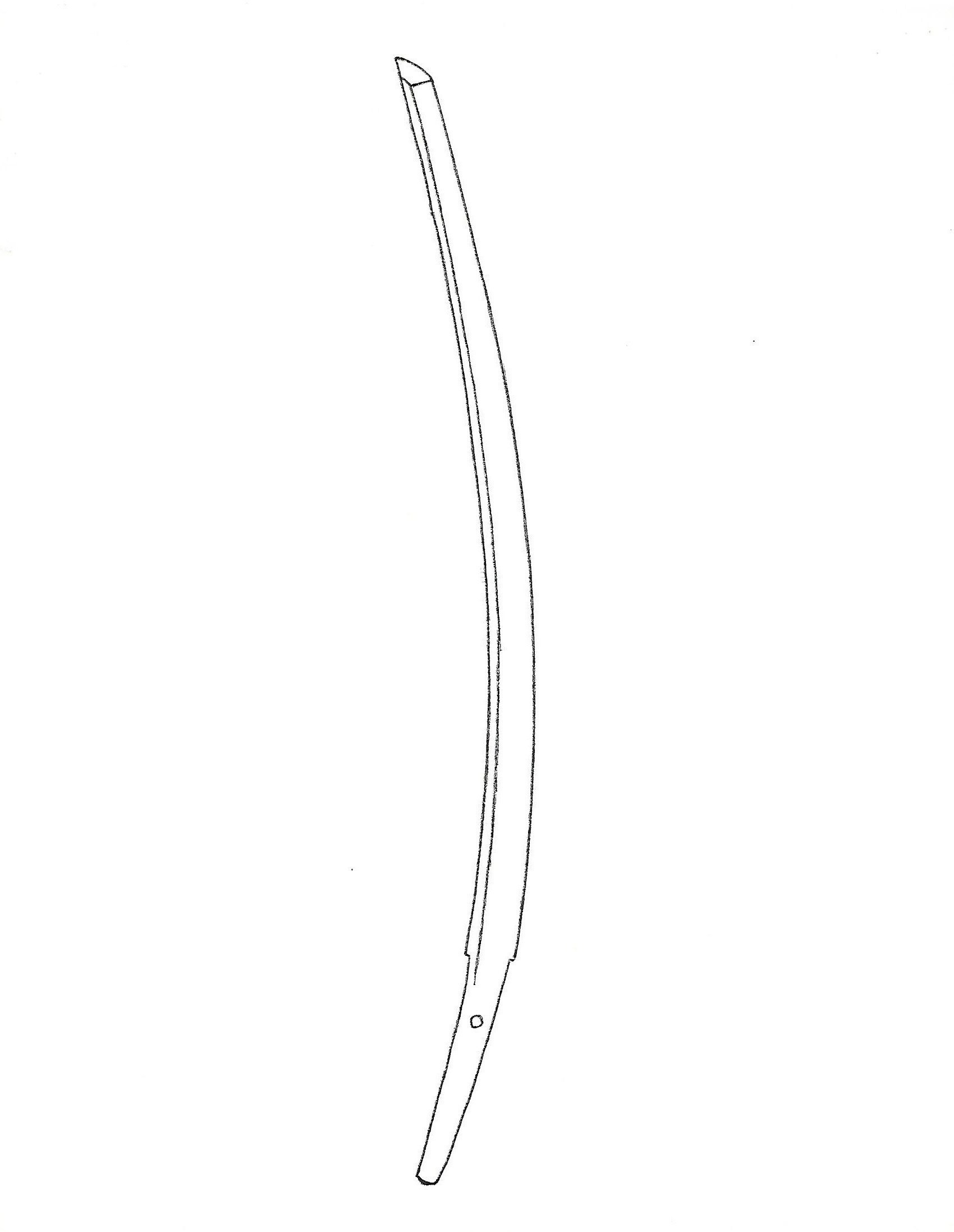
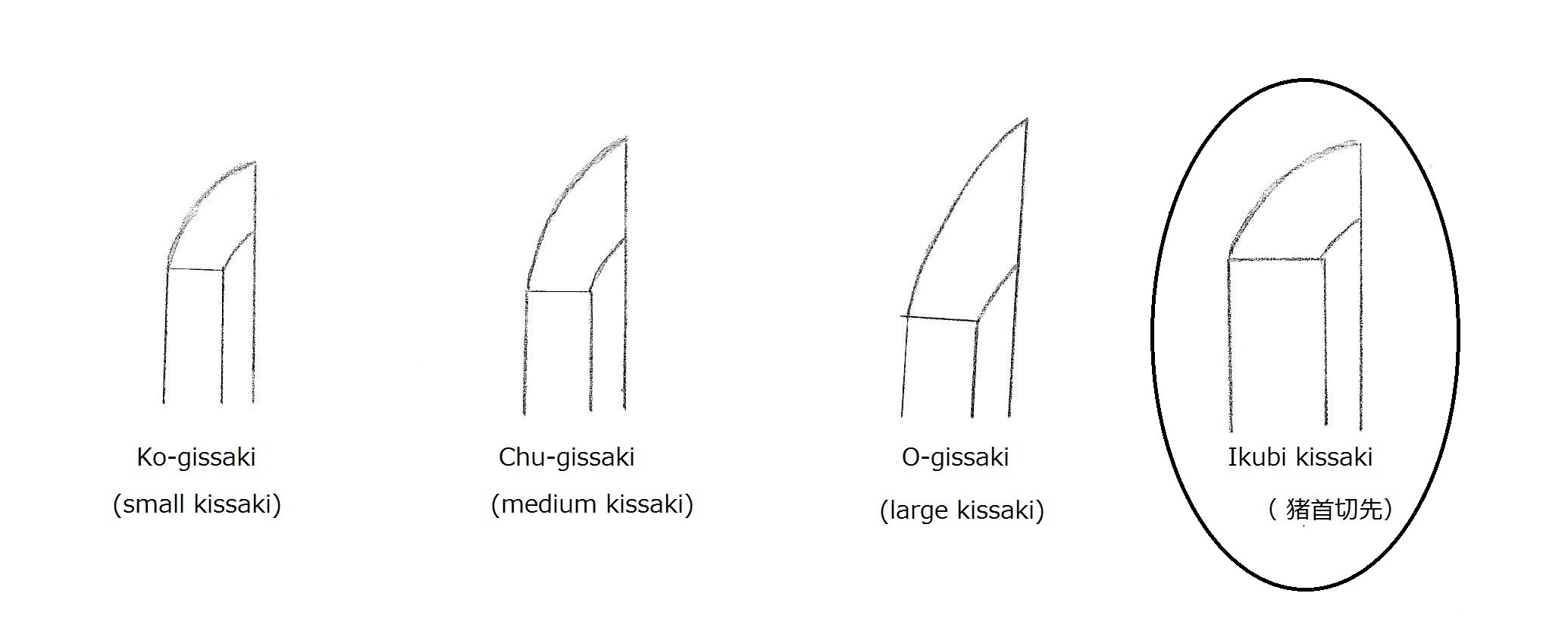
Sugata (shape) —————–Generally, a gentle or graceful kyo-zori shape. The difference in width between the yokote line and the machi is minimal. The sword is slender, yet thick, with a small kissaki.
Hi and Engraving ———————– Bo-hi (single groove) or futasuji-hi (double grooves)
Hamon ——————— Nie base with ko-choji (small clove shape) and ko-midare (small irregular). Small inazuma (lightning-like lines) and kinsuji (golden streaks) may be present. Double ko-choji (two ko-choji side by side) may appear.
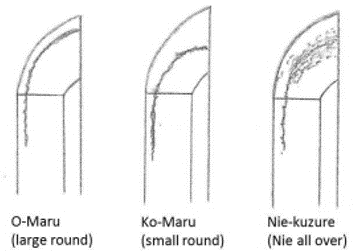
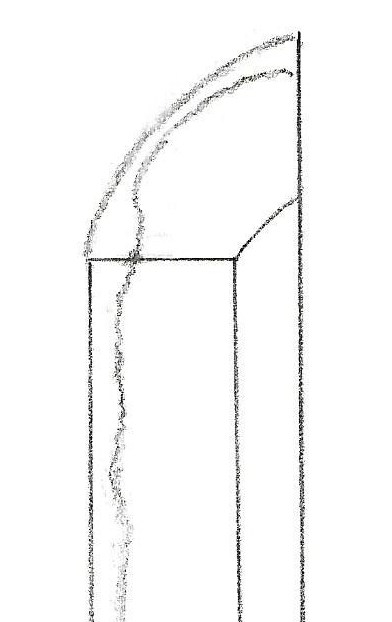
Boshi (tempered line at the kissaki area) ———————– Ko-maru (small round), yakizume (see the illustration below ), and kaen (flame-like pattern)
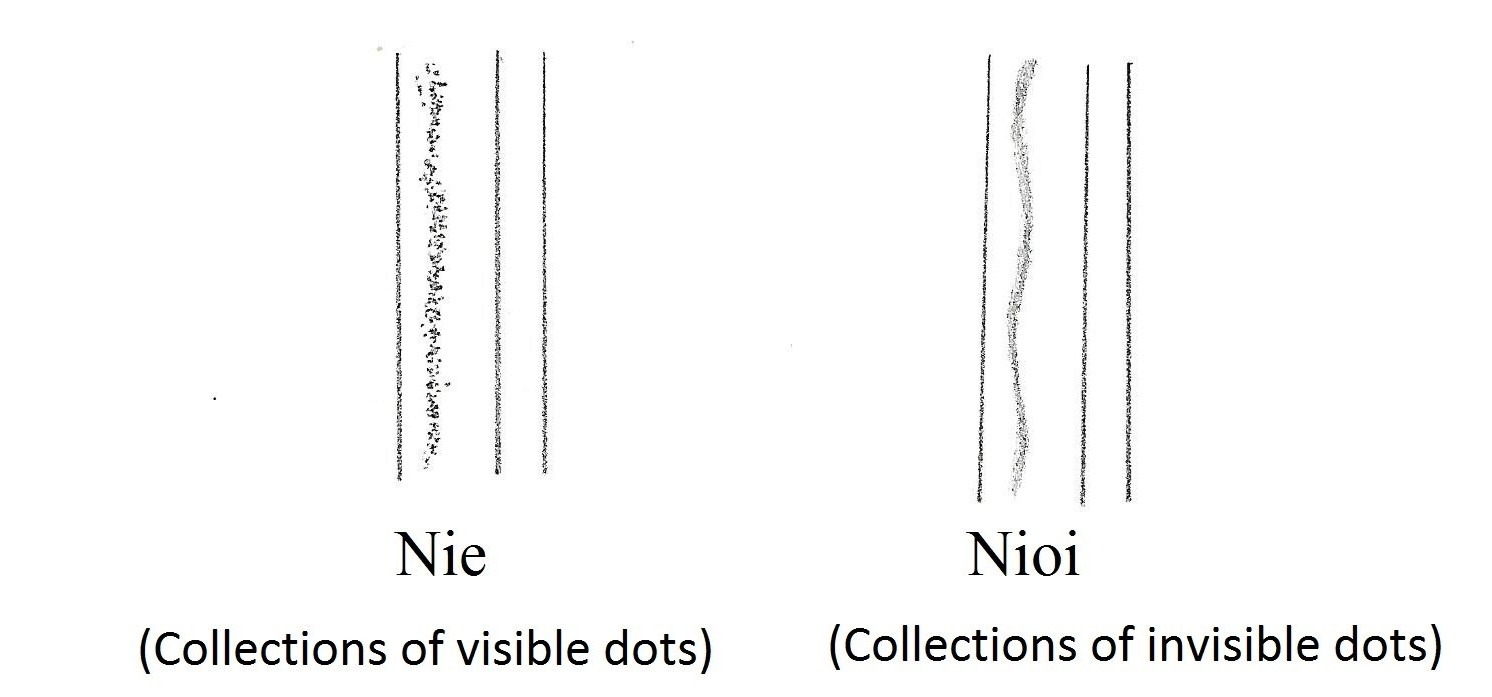
Ji-hada —————– Small wood grain with a little masame (straight grain). Ji-nie shows.
Nakago (hilt) ———————— Long, slightly thick feel
Ayano-koji Ippa swordsmiths ———-Ayano-koji Sadatoshi (綾小路定利) Sadanori (定則)
Awataguchi Ichimon (粟田口)
Many swordsmiths from the Awataguchi Ichimon (or Awataguchi group) were honored as the Goban Kaji (the top swordsmith) by Gotoba Joko, Emperor Gotoba (後鳥羽上皇). Their general characteristics are as follows.
Sugata (Shape) ————————- Elegant torii-zori (or kyo-zori) shape.
Hi and Engraving ————– The tip of the hi extends all the way up and fills in the ko-shinogi. The end of the hi can be maru-dome (the end is round), kaku-dome (the end is square), or kakinagashi.
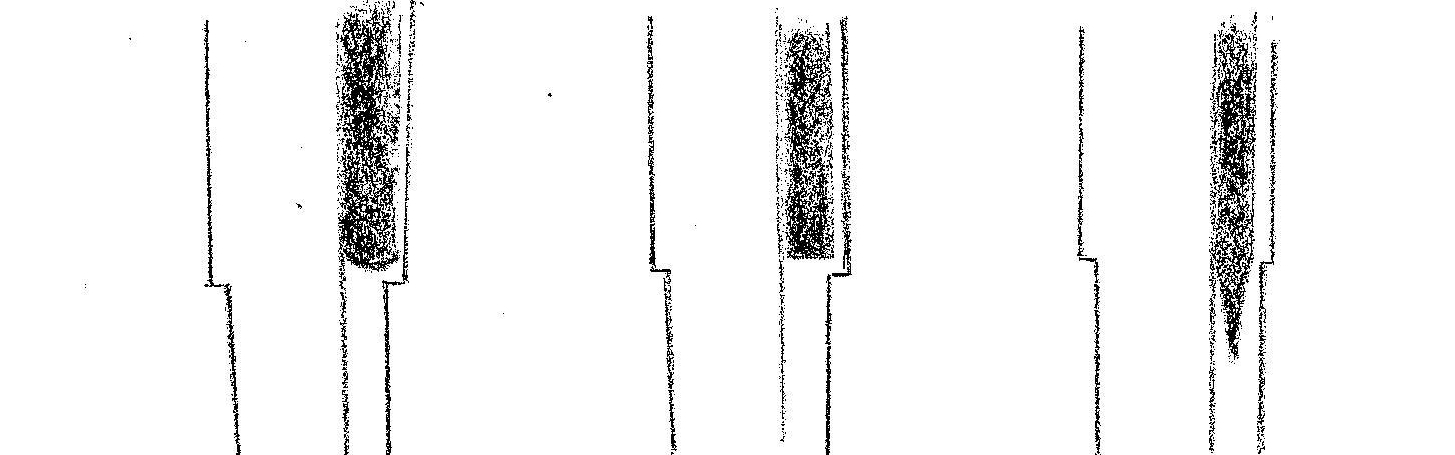
Maru-dome (rounded end) Kaku-dome (square) Kakinagashi
-
Hamon ———— The slightly wider tempered line at the bottom, then it becomes narrower at the top. Nie base (called Nie-hon’i). A straight tempered line mixed with ko-choji (small cloves) or a wide straight line combined with choji. Awataguchi-nie appears. Awataguchi-nie, which refers to a fine, deep, sharp, shiny nie that appears around the tempered line area. Fine inazuma (lightning-like lines) and kinsuji (golden streaks) emerge.
- Boshi (tempered line at the tip area) —————— Ko-maru (small round) and/or O-maru (large round). The return is sharrow. Yakizume, Nie Kuzure, and Kaen (flame)

Yakizume O-maru Ko-maru Yakikuzure
- Ji-hada ————– Fine ko-mokume (wood swirls) with ji-nie. Ji-nie is nie on ji-hada. Yubashiri and/or chikei appear.
- Nakago ——————————– Often featuresa two-letter inscription
- Names of Awataguchi swordsmiths —– Awataguchi Kunitomo (粟田口国友 ), Hisakuni (久国), Kuniyasu (国安), Kuniyasu (国安), Kunikiyo (国清)
Rai Ha (来)
The general characteristics of the Rai group are as follows. However, each swordsmith has their own unique traits.
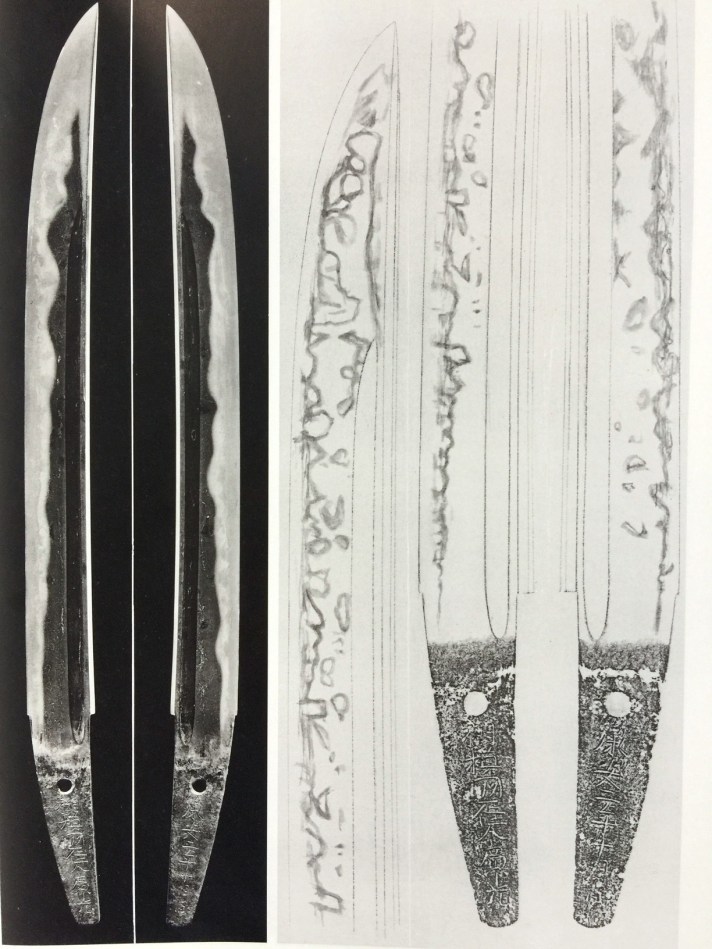
Sugata (shape) ——– Graceful and dignified. Thick body. Rai forged Ikubi Kissaki. Hi and Engravings ————————- Wide and shallow hi. Hamon ————————- Nie base. Suguha (straight). Wide suguha with ko-midare (small irregular) and choji (cloves). Sometimes, there is a large choji at the lower part and a narrow suguha at the top. Inazuma and Kinsuji appear around the yokote area. Boshi ————————————- Komaru, yakizume (see the illustration above) Ji-hada ——————— Finely forged itame (small wood grain). Sometimes mixed with masame (parallel grain). Fine nie. Rai group’s swords occasionally show yowai tetsu (weak surface), which may be the core iron.
Rai Ha swordsmiths———————- Rai Kuniyuki (来国行), Rai Kunitoshi (来国俊) or Niji Kunitoshi (二字国俊), Ryokai (了戒 ). Rai Kunitoshi is said to be the son of Rai Kuniyuki. Ryokai is said to be the son of Rai Kunitoshi.

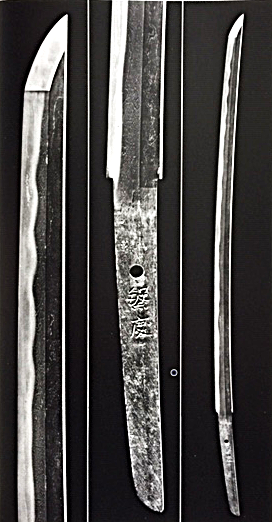
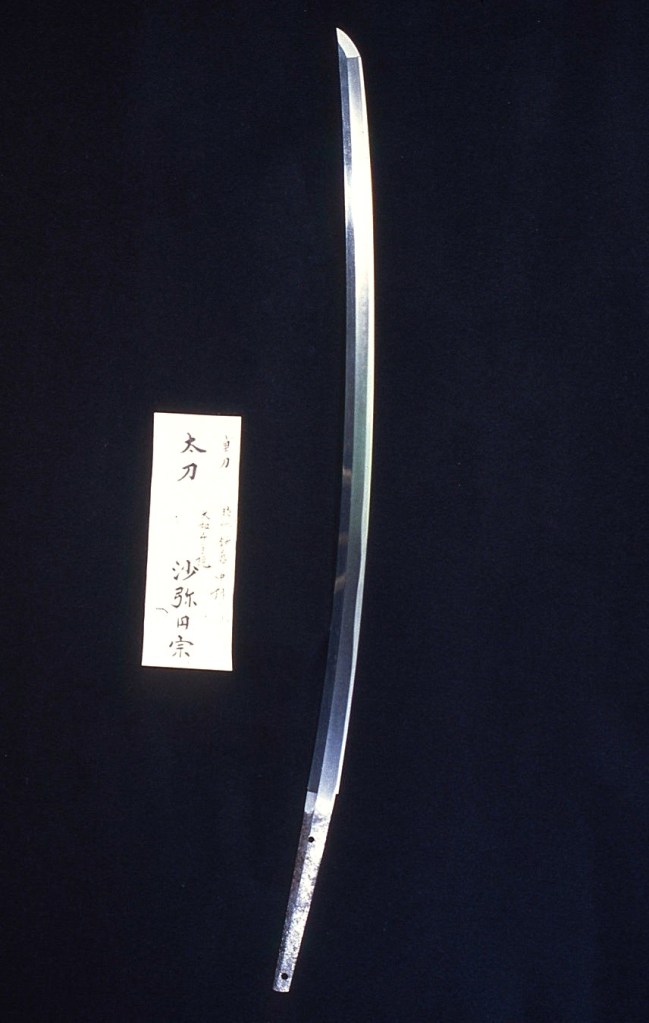
Rai Kuniyuki (来国行)Once my family sword, photo taken by my father with his writing.
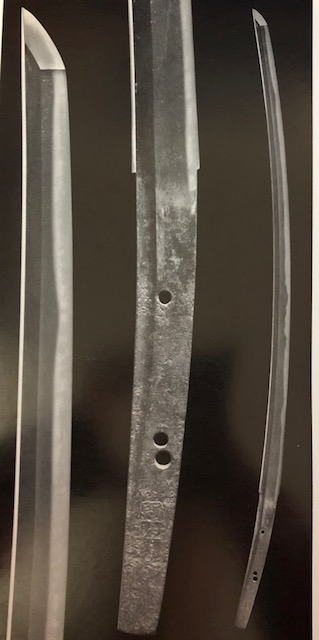

Rai Kuniyuki (来国行)Sano Museum Catalogue (佐野美術館) (permission granted)








































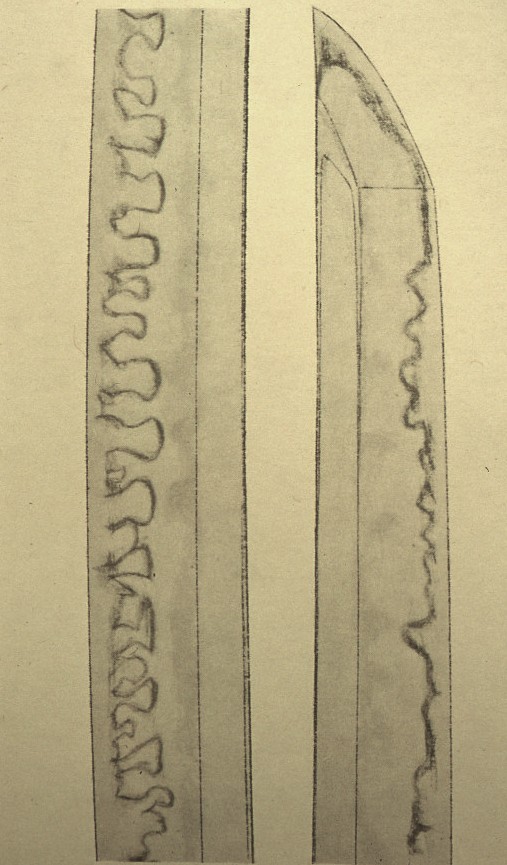
 Kawazuko-choji O-choji Ko-choji Suguha-choji (tadpole head) (large clove) (small clove) (straight and clove)
Kawazuko-choji O-choji Ko-choji Suguha-choji (tadpole head) (large clove) (small clove) (straight and clove)
 Sansaku-boshi
Sansaku-boshi
 Osafune Nagamitsu(長船長光) From Sano Museum Catalogue (permission granted)
Osafune Nagamitsu(長船長光) From Sano Museum Catalogue (permission granted) 
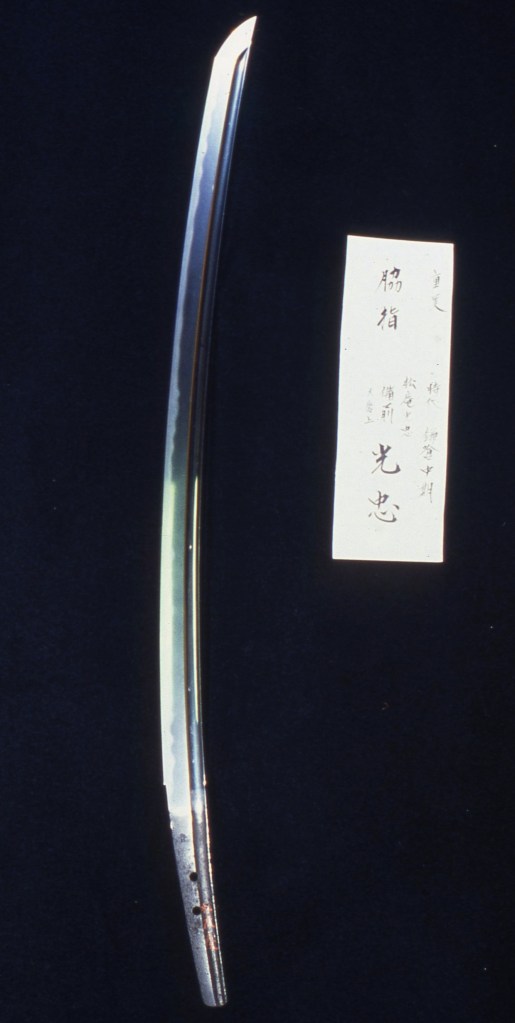 Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠) Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠)
Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠) Osafune Mitsutada(長船光忠)